Knee pain is one of the most common musculoskeletal complaints worldwide. It affects people across all age groups—from teenagers involved in sports to adults working long hours on their feet, and seniors experiencing age-related changes. According to medical studies, over one in four adults suffer from frequent knee pain, making it a leading reason for reduced mobility and doctor visits.
While some knee conditions require medical treatment, the majority of cases are linked to lifestyle factors such as posture, muscle weakness, or overuse. This means that with the right knowledge and tools, many people can manage and reduce knee discomfort naturally at home.
Understanding the Structure of the Knee
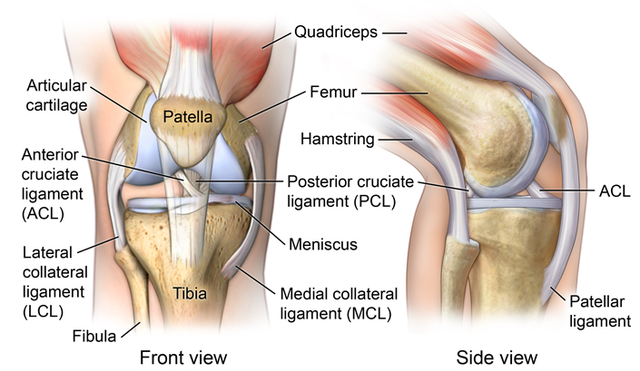
The knee is the largest and one of the most complex joints in the human body. It connects the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia), supported by ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. This structure allows for flexibility and strength—but also makes the knee vulnerable to injury and wear.
Key components include:
-
Cartilage: Cushions the bones and reduces friction.
-
Ligaments: Stabilize the knee joint.
-
Tendons: Connect muscles to bones and support movement.
-
Meniscus: A shock-absorbing structure that protects the joint.
Any disruption to these elements can lead to pain, stiffness, or reduced function.
Common Causes of Knee Pain
-
Overuse and Repetitive Stress
High-impact activities like running, jumping, or climbing can overload the knee. Repetitive motions in sports or certain jobs also contribute. -
Muscle Weakness and Imbalance
Weak quadriceps, hamstrings, or glute muscles force the knee to absorb excess stress, causing strain and misalignment. -
Acute Injuries
Sprains, ligament tears (ACL, MCL), or meniscus injuries are common in athletes but can happen to anyone after sudden twisting or falls. -
Degenerative Conditions
Osteoarthritis is a major cause of knee pain in older adults. It develops when cartilage wears down, leading to stiffness, swelling, and limited motion. -
Posture and Foot Mechanics
Flat feet, poor footwear, or abnormal walking patterns can shift weight unevenly, placing strain on the knees.
Risk Factors for Knee Pain
While anyone can experience knee pain, some risk factors increase the likelihood:
-
Age – cartilage and ligaments weaken over time
-
Obesity – extra body weight adds stress to the joints
-
Occupation – jobs involving kneeling, lifting, or prolonged standing
-
Sports participation – high-impact or contact sports increase risk of injury
-
Previous injuries – past damage to the knee makes recurrence more likely
Recognizing Symptoms
Knee pain can range from mild discomfort to debilitating immobility. Common symptoms include:
-
Persistent aching or throbbing around the joint
-
Swelling and stiffness after activity
-
Sharp or stabbing pain when bending, squatting, or climbing stairs
-
Clicking, grinding, or popping sounds
-
Instability or the feeling that the knee may “give out”
-
Pain radiating into the thigh or calf
Identifying these symptoms early can help prevent worsening conditions.
Natural Relief Methods for Knee Pain
Fortunately, research shows that many cases of knee pain can be managed effectively with conservative, natural strategies.
1. Strengthening and Flexibility Exercises
-
Strengthening quadriceps, hamstrings, and hip muscles helps stabilize the knee.
-
Low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, or yoga improve mobility without overloading the joint.
-
Resistance bands on a yoga mat are great tools for safe at-home exercise.
2. Compression Therapy
-
Compression socks or knee sleeves reduce swelling, support circulation, and provide stability.
-
Particularly effective for people who stand for long periods or have age-related joint issues.
3. Massage and Heat/Cold Therapy
-
Massage around the thighs, calves, and knee area relieves muscle tension.
-
Heat therapy helps with stiffness, while cold therapy reduces inflammation after activity.
4. Weight and Lifestyle Management
-
Maintaining a healthy weight decreases joint load.
-
Incorporating stretching breaks into daily routines prevents stiffness from prolonged sitting.
5. Posture and Foot Alignment
-
Proper footwear with good arch support reduces uneven stress.
-
Orthotic insoles may help correct gait issues.
When to Seek Professional Help
Although many people find relief with home remedies, consult a healthcare professional if:
-
Pain persists beyond two weeks despite self-care
-
The knee suddenly locks, clicks, or swells severely
-
You experience instability or difficulty bearing weight
-
Pain is accompanied by fever, redness, or warmth around the joint
These may signal more serious conditions requiring medical evaluation.
Conclusion
Knee pain is widespread but manageable. By combining strengthening exercises, massage, compression support, and proper posture, you can significantly reduce discomfort and protect long-term joint health.
At WellZonez, we believe in empowering people with natural, effective solutions. That’s why we offer a carefully curated range of compression socks, yoga mats, resistance bands, and massage devices—all designed to support mobility, reduce pain, and improve daily living.
👉 Explore the WellZonez collection today and take confident steps toward stronger, healthier knees.


0 comments